最新下载
热门教程
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
vue-cli V3.0版本的使用详解
时间:2022-06-25 15:31:57 编辑:袖梨 来源:一聚教程网
vue-cli 3.0版本
目前官网上还不是3.0版本,所以需要在github上面学习使用:github网站:https://github.com/vuejs/vue-cli/tree/dev/docs
1、项目搭建
(1)、在上面的GitHub网页中,拉到底部可以看到:
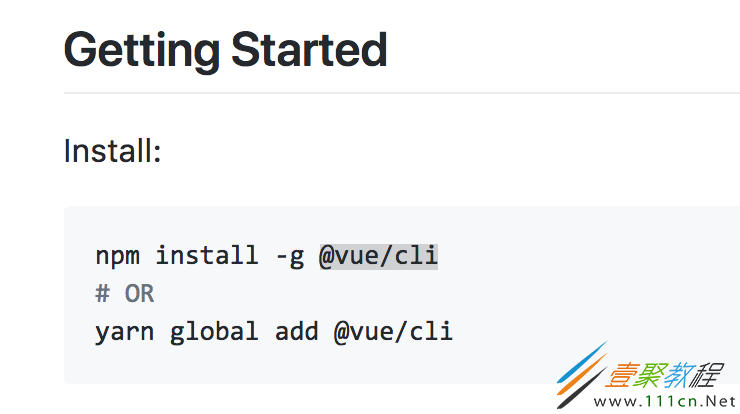
然后在全局中执行命令:sudo npm install -g @vue/cli即可。
最后,
vue -V //可以查看到当前的vue是3.0版本了
(2)、查看vue 相关指令
vue --help
查看到的常用指令:
-V:查看版本号
-h:
create:创建一个项目
add: 在项目中创建插件(相当于之前的 "npm install")
invoke:在已创建好的项目中调用插件
inspect:检查webpack配置
serve:开发环境——npm run serve(相当于之前的npm run dev)
build:生产环境,打包上线的
ui:调用一个ui库
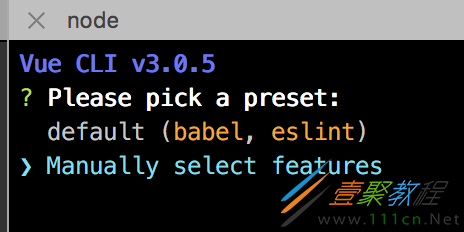
(3)、创建项目
//执行: vue create vue2-demo
在下面的选项中选择Manually select features,点击enter后,在显示的列表中通过上下键+空格选择需要的插件。下面根据需要选择即可。
(4)、依次按照下面的步骤创建一个专属的脚手架,这样下次创建项目的时候就能直接使用“testnewcli”这个脚手架了。
// vue.config.js 配置说明
// 这里只列一部分,具体配置惨考文档啊
module.exports = {
// baseUrl type:{string} default:'/'
// 将部署应用程序的基本URL
// 将部署应用程序的基本URL。
// 默认情况下,Vue CLI假设您的应用程序将部署在域的根目录下。
// https://www.my-app.com/。如果应用程序部署在子路径上,则需要使用此选项指定子路径。例如,如果您的应用程序部署在https://www.foobar.com/my-app/,集baseUrl到'/my-app/'.
baseUrl: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? '/online/' : '/',
// outputDir: 在npm run build时 生成文件的目录 type:string, default:'dist'
// outputDir: 'dist',
// pages:{ type:Object,Default:undfind }
/*
构建多页面模式的应用程序.每个“页面”都应该有一个相应的JavaScript条目文件。该值应该是一
个对象,其中键是条目的名称,而该值要么是指定其条目、模板和文件名的对象,要么是指定其条目
的字符串,
注意:请保证pages里配置的路径和文件名 在你的文档目录都存在 否则启动服务会报错的
*/
// pages: {
// index: {
// entry for the page
// entry: 'src/index/main.js',
// the source template
// template: 'public/index.html',
// output as dist/index.html
// filename: 'index.html'
// },
// when using the entry-only string format,
// template is inferred to be `public/subpage.html`
// and falls back to `public/index.html` if not found.
// Output filename is inferred to be `subpage.html`.
// subpage: 'src/subpage/main.js'
// },
// lintOnSave:{ type:Boolean default:true } 问你是否使用eslint
lintOnSave: true,
// productionSourceMap:{ type:Bollean,default:true } 生产源映射
// 如果您不需要生产时的源映射,那么将此设置为false可以加速生产构建
productionSourceMap: false,
// devServer:{type:Object} 3个属性host,port,https
// 它支持webPack-dev-server的所有选项
devServer: {
port: 8085, // 端口号
host: 'localhost',
https: false, // https:{type:Boolean}
open: true, //配置自动启动浏览器
// proxy: 'http://localhost:4000' // 配置跨域处理,只有一个代理
proxy: {
'/api': {
target: '',
ws: true,
changeOrigin: true
},
'/foo': {
target: ''
}
}, // 配置多个代理
}
}
2、添加插件(新版本提供的添加方法)
/添加插件的新方法:vue add vue add vuetify
注:如果我们安装的是模块依赖,建议使用npm install ;如果安装的是组件UI,可能会对当前的页面UI有影响的情况下,就使用vue add方法安装。
比如上面的vuetify是一个vue的UI库,会对页面结构布局产生影响,所以使用vue add 方法;比如我们安装axios插件,就是用npm install axios就可以了。
3、全局环境变量
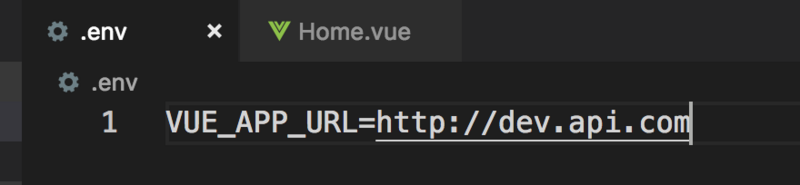
(1)、创建".env"文件:
(2)、在组件中使用全局变量
{{url}}
4、独立运行.vue文件
如上图中,在根目录下创建的"hello.vue"文件如何独立运行起来呢?(不依赖脚手架)
//可行方案:安装插件 sudo npm install -g @vue/cli-service-global //之后执行命令: vue serve hello.vue //这样就可以在浏览器看到hello.vue相对应的页面了
5、配置的基础路径(vue.config.js)
根目录创建文件"vue.config.js",
//vue.config.js中配置
module.exports = {
baseUrl: "/", //根路径
outputDir: "dist", //构建输出目录,执行:npm run build后项目打包在dist文件下
assetsDir: "assets", //静态资源目录(js,css,img,fonts)
linitOnSave: false, //是否开启eslint保存检测,有效值:true || false || "error"
}
6、配置跨域请求
在vue.config.js中进行配置:
module.exports = {
baseUrl: "/", //根路径
outputDir: "dists", //构建输出目录
assetsDir: "assets", //静态资源目录(js,css,img,fonts)
lintOnSave: false, //是否开启eslint保存检测,有效值:true || false || "error"
devServer: {
open: true, //浏览器自动打开页面
host: '127.0.0.0', //域名
//host: "0.0.0.0", //如果是真机测试,就使用这个IP
port: 8060,
https: false,
hotOnly: false, //热更新(webpack已实现了,这里false即可)
proxy: {
//配置跨域
'/api': {
target: "http://localhost:2020/api",
ws:true,
changOrigin:true,
pathRewrite:{
'^/api':''
}
}
}
}
}
7、加载json数据
根目录下创建data文件夹,里面包含文件data.json,然后在vue.config.js文件中进行配置。
const goods = require("./data/goods.json");
module.exports = {
baseUrl: "/", //根路径
outputDir: "dists", //构建输出目录
assetsDir: "assets", //静态资源目录(js,css,img,fonts)
lintOnSave: false, //是否开启eslint保存检测,有效值:true || false || "error"
devServer: {
open: true, //浏览器自动打开页面
host: 'localhost', //域名
port: 8060,
https: false,
hotOnly: false, //热更新(webpack已实现了,这里false即可)
//加载本地josn数据
//参见webpack官网:https://webpack.docschina.org/configuration/dev-server/#devserver-before
before(app) {
//http://localhost:8090/myapi/goods
app.get("/myapi/goods", (req, res) => {
res.json(goods);
})
}
}
}
相关文章
- 价格跟踪交易-价格跟踪交易软件 04-25
- 碧蓝航线使用要注意什么 04-25
- 明日之后苹果能做什么食物攻略 04-25
- 以闪亮之名浅栗捏脸数据id攻略 04-25
- 逆水寒手游春归学堂奇遇如何完成 04-25
- 明日之后二层别墅建造蓝图攻略 04-25