最新下载
热门教程
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Python中jieba库的使用方法代码示例
时间:2022-06-25 01:55:57 编辑:袖梨 来源:一聚教程网
本篇文章小编给大家分享一下Python中jieba库的使用方法代码示例,文章代码介绍的很详细,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家供大家参考,有需要的小伙伴们可以来看看。
jieba库是一款优秀的 Python 第三方中文分词库,jieba支持三种分词模式:精确模式、全模式和搜索引擎模式,下面是三种模式的特点。
精确模式:试图将语句最精确的切分,不存在冗余数据,适合做文本分析
全模式:将语句中所有可能是词的词语都切分出来,速度很快,但是存在冗余数据
搜索引擎模式:在精确模式的基础上,对长词再次进行切分
一、jieba库的安装
因为jieba是一个第三方库,所有需要我们在本地进行安装。
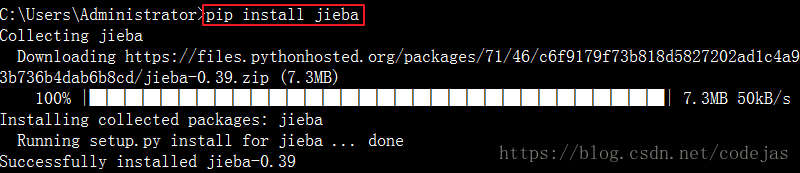
Windows 下使用命令安装:在联网状态下,在命令行下输入pip install jieba进行安装,安装完成后会提示安装成功
在 pyCharm 中安装:打开settings,搜索Project Interpreter,在右边的窗口选择+号,点击后在搜索框搜索jieba,点击安装即可
二、jieba三种模式的使用
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import jieba
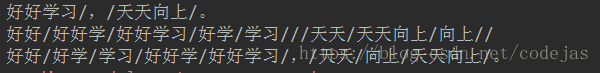
seg_str = "好好学习,天天向上。"
print("/".join(jieba.lcut(seg_str))) # 精简模式,返回一个列表类型的结果
print("/".join(jieba.lcut(seg_str, cut_all=True))) # 全模式,使用 'cut_all=True' 指定
print("/".join(jieba.lcut_for_search(seg_str))) # 搜索引擎模式
分词效果:
三、jieba 分词简单应用
需求:使用jieba分词对一个文本进行分词,统计次数出现最多的词语,这里以三国演义为例
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import jieba
txt = open("三国演义.txt", "r", encoding='utf-8').read()
words = jieba.lcut(txt) # 使用精确模式对文本进行分词
counts = {} # 通过键值对的形式存储词语及其出现的次数
for word in words:
if len(word) == 1: # 单个词语不计算在内
continue
else:
counts[word] = counts.get(word, 0) + 1 # 遍历所有词语,每出现一次其对应的值加 1
items = list(counts.items())
items.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) # 根据词语出现的次数进行从大到小排序
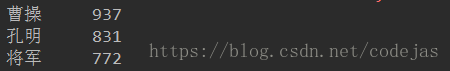
for i in range(3):
word, count = items[i]
print("{0:5}".format(word, count))
统计结果:
你可以随便找一个文本文档,也可以到https://git**h*ub.com/coderjas/python-quick下载上面例子中的文档。
四、扩展:英文单词统计
上面的例子统计实现了中文文档中出现最多的词语,接着我们就来统计一下一个英文文档中出现次数最多的单词。原理同上
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
def get_text():
txt = open("1.txt", "r", encoding='UTF-8').read()
txt = txt.lower()
for ch in '!"#$%&()*+,-./:;?@[]^_‘{|}~':
txt = txt.replace(ch, " ") # 将文本中特殊字符替换为空格
return txt
file_txt = get_text()
words = file_txt.split() # 对字符串进行分割,获得单词列表
counts = {}
for word in words:
if len(word) == 1:
continue
else:
counts[word] = counts.get(word, 0) + 1
items = list(counts.items())
items.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
for i in range(5):
word, count = items[i]
print("{0:{1:>5}".format(word, count))
统计结果:
相关文章
- 流放之路2全部高价值传奇物品汇总 10-24
- 流放之路2凛冬狼的头颅获取方法分享 10-24
- 流放之路2远古誓言任务攻略分享 10-24
- 流放之路2全部地图隐藏奖励介绍说明 10-24
- 流放之路2通货E是什么 通货E介绍说明 10-24
- 夺宝奇兵渲染器设置错误解决方法分享 10-24