最新下载
热门教程
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
python实现三阶魔方还原代码示例
时间:2022-06-25 02:04:10 编辑:袖梨 来源:一聚教程网
本篇文章小编给大家分享一下python实现三阶魔方还原代码示例,文章代码介绍的很详细,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家供大家参考,有需要的小伙伴们可以来看看。
思路
复原魔方困难问题的分解:
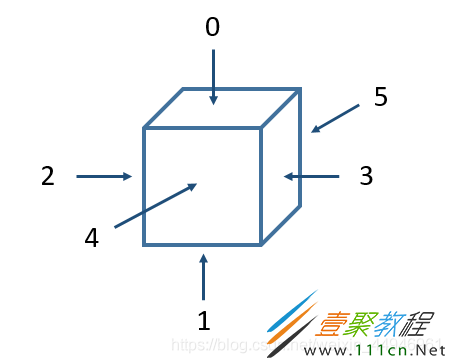
1、用合适的数据结构表示出三阶魔方的六个面以及每一面的颜色
2、每一次不同旋转操作的实现
3、复原时如何判断当前魔方应该使用哪一种公式
本次实验实现了前两个操作,具体思路是:
用numpy库中的矩阵将六个面分别表示出来,按上下左右前后的顺序放入列表中。再依据流行公式里的方法编写对每一个面进行旋转操作的函数,调用函数实现魔方的旋转。最后输入指令可得到旋转之后的魔方,以及执行逆序指令后验证魔方还原。
预备知识
矩阵:使用numpy库中的矩阵结构
函数说明:
U: 上面顺时针旋转 90°
D: 底面顺时针旋转 90°
L: 左面顺时针旋转 90°
R: 右面顺时针旋转 90°
F: 正面顺时针旋转 90°
B: 背面顺时针旋转 90°
**注:**字母前加上下划线 ‘_' 表示逆时针
代码详解
本次实验将【上、下、左、右、前、后】六个面用数字【0、1、2、3、4、5】表示原本每个面的颜色,并依次存入列表faces【】里(即:faces[0]中存放的是最上面的数字全为0的三阶矩阵)
注:魔方视角始终固定,即在整个过程中正(左…)面始终是正(左…)面
# 创建六个面,放在faces列表里,顺序为上(0),下(1),左(2),右(3),前(4),后(5)
faces = [np.zeros((3, 3))]
for i in range(1, 6):
faces.append(np.ones((3, 3)) + faces[i - 1])
每一个面的顺时针和逆时针旋转由函数clockwise()和antiClockwise()实现
t = np.array([[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0]])
# 该面顺时针旋转 90 度
def clockwise(face):
face = face.transpose().dot(t)
return face
# 该面逆时针旋转 90 度
def antiClockwise(face):
face = face.dot(t).transpose()
return face
A.transpose() 方法是实现 A 矩阵的转置
A.dot(B) 方法是实现 A乘以矩阵B
通过计算,上述方法可以实现矩阵顺时针或者逆时针旋转的效果
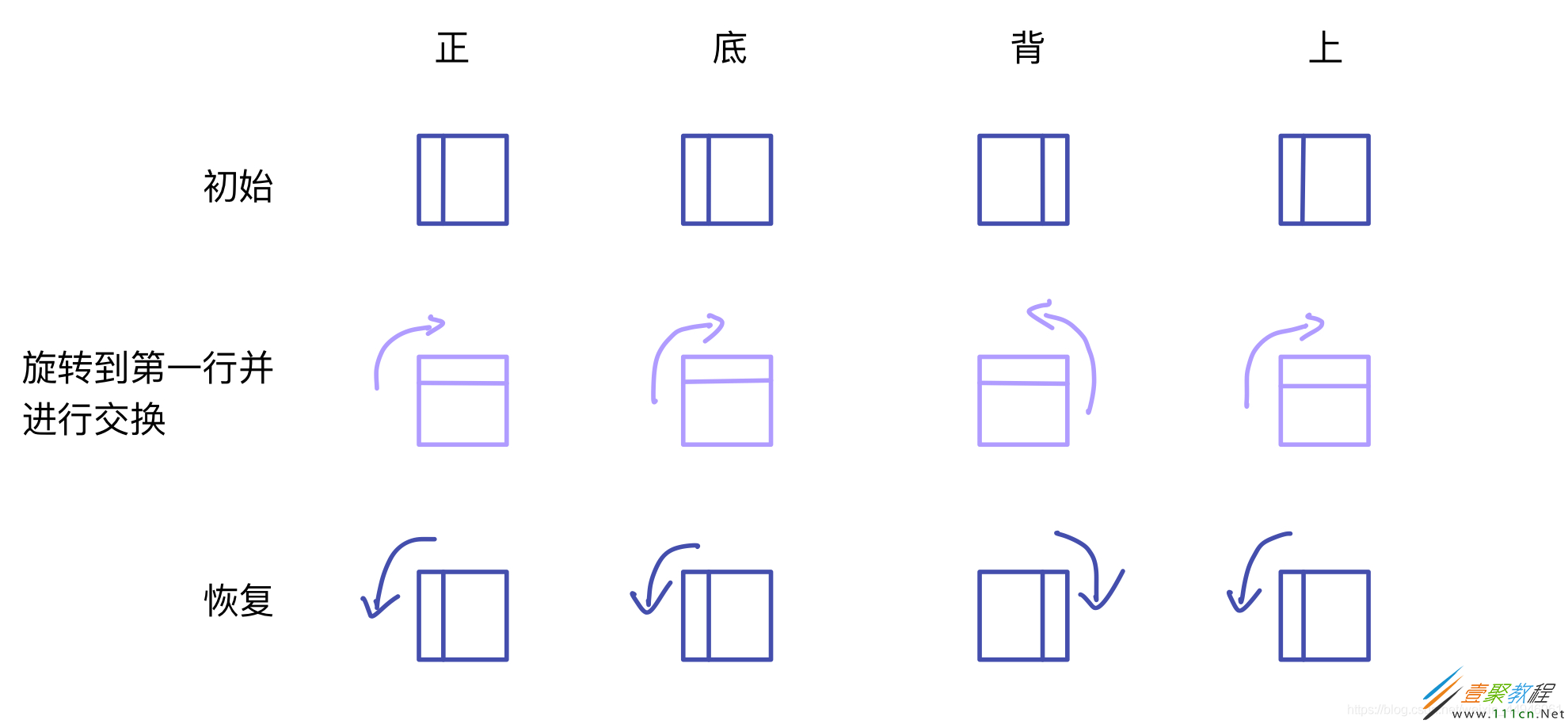
在这里以左面的顺时针旋转 90°为例,其它旋转方式可以类比
def L(FACES):
FACES[2] = clockwise(FACES[2])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = clockwise(FACES_new[4]), clockwise(FACES_new[1]), antiClockwise(FACES_new[5]), clockwise(FACES_new[0])
e, f, g, h = cp.deepcopy(a), cp.deepcopy(b), cp.deepcopy(c), cp.deepcopy(d)
e[0], f[0], g[0], h[0] = d[0], a[0], b[0], c[0]
FACES[4], FACES[1], FACES[5], FACES[0] = antiClockwise(e), antiClockwise(f), clockwise(g), antiClockwise(h)
1、直接调用函数将左面(第2面)顺时针旋转 90°
FACES[2] = clockwise(FACES[2])
2、这里采用深度复制,使用 cp.deepcopy() 的方法,避免直接使用等号 ‘=' 导致不同的变量指向同一个值。这时,【e、f、g、h】和【a、b、c、d】代表魔方的
【正面、底面顺时针旋转90°、背面逆时针旋转90°、上面顺时针旋转90°】
a, b, c, d = clockwise(FACES_new[4]), clockwise(FACES_new[1]), antiClockwise(FACES_new[5]), clockwise(FACES_new[0])
旋转的目的是:
在左面旋转的过程中,左面会影响到其它四个面,但对其它四个面的影响是不同的。例如正面、底面和上面被影响的是第一列,而背面被影响的是第三列。我们为了使各面统一起来,方便数值的改变,我们选择将正、底、上面顺时针旋转90°,将背面逆时针旋转90°。这时,我们只需按顺序交换每一面的第一行,最后再逆时针或顺时针转回来即可。
3、按顺序交换:正面第一行传递到底面第一行
上面第一行传递到正面第一行
背面第一行传递到上面第一行
底面第一行传递到背面第一行
e[0], f[0], g[0], h[0] = d[0], a[0], b[0], c[0]
最后再依次根据上述操作逆旋转回去:
FACES[4], FACES[1], FACES[5], FACES[0] = antiClockwise(e), antiClockwise(f), clockwise(g), antiClockwise(h)
代码
import numpy as np
import copy as cp
# 创建六个面,放在faces列表里,顺序为上(0),下(1),左(2),右(3),前(4),后(5)
faces = [np.zeros((3, 3))]
for i in range(1, 6):
faces.append(np.ones((3, 3)) + faces[i - 1])
t = np.array([[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0]])
# 该面顺时针旋转 90 度
def clockwise(face):
face = face.transpose().dot(t)
return face
# 该面逆时针旋转 90 度
def antiClockwise(face):
face = face.dot(t).transpose()
return face
def U(FACES):
FACES[0] = clockwise(FACES[0])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = FACES_new[4], FACES_new[2], FACES_new[5], FACES_new[3]
FACES[4][0], FACES[2][0], FACES[5][0], FACES[3][0] = d[0], a[0], b[0], c[0]
def _U(FACES):
FACES[0] = antiClockwise(FACES[0])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = FACES_new[4], FACES_new[2], FACES_new[5], FACES_new[3]
FACES[4][0], FACES[2][0], FACES[5][0], FACES[3][0] = b[0], c[0], d[0], a[0]
def U2(FACES):
for i in range(2):
U(FACES)
'''
FACES[0] = clockwise(clockwise(FACES[0]))
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = FACES_new[4], FACES_new[2], FACES_new[5], FACES_new[3]
FACES[4][0], FACES[2][0], FACES[5][0], FACES[3][0] = c[0], d[0], a[0], b[0]
'''
def D(FACES):
FACES[1] = clockwise(FACES[1])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = FACES_new[4], FACES_new[2], FACES_new[5], FACES_new[3]
FACES[4][2], FACES[2][2], FACES[5][2], FACES[3][2] = b[2], c[2], d[2], a[2]
def _D(FACES):
FACES[1] = antiClockwise(FACES[1])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = FACES_new[4], FACES_new[2], FACES_new[5], FACES_new[3]
FACES[4][2], FACES[2][2], FACES[5][2], FACES[3][2] = d[2], a[2], b[2], c[2]
def D2(FACES):
for i in range(2):
D(FACES)
'''
FACES[1] = clockwise(clockwise(FACES[1]))
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = FACES_new[4], FACES_new[2], FACES_new[5], FACES_new[3]
FACES[4][2], FACES[2][2], FACES[5][2], FACES[3][2] = c[2], d[2], a[2], b[2]
'''
def L(FACES):
FACES[2] = clockwise(FACES[2])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = clockwise(FACES_new[4]), clockwise(FACES_new[1]), antiClockwise(FACES_new[5]), clockwise(FACES_new[0])
e, f, g, h = cp.deepcopy(a), cp.deepcopy(b), cp.deepcopy(c), cp.deepcopy(d)
e[0], f[0], g[0], h[0] = d[0], a[0], b[0], c[0]
FACES[4], FACES[1], FACES[5], FACES[0] = antiClockwise(e), antiClockwise(f), clockwise(g), antiClockwise(h)
def _L(FACES):
FACES[2] = antiClockwise(FACES[2])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = clockwise(FACES_new[4]), clockwise(FACES_new[1]), antiClockwise(FACES_new[5]), clockwise(FACES_new[0])
e, f, g, h = cp.deepcopy(a), cp.deepcopy(b), cp.deepcopy(c), cp.deepcopy(d)
e[0], f[0], g[0], h[0] = b[0], c[0], d[0], a[0]
FACES[4], FACES[1], FACES[5], FACES[0] = antiClockwise(e), antiClockwise(f), clockwise(g), antiClockwise(h)
def L2(FACES):
for i in range(2):
L(FACES)
# 上(0),下(1),左(2),右(3),前(4),后(5)
def R(FACES):
FACES[3] = clockwise(FACES[3])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = antiClockwise(FACES_new[4]), antiClockwise(FACES_new[1]), clockwise(FACES_new[5]), antiClockwise(
FACES_new[0])
e, f, g, h = cp.deepcopy(a), cp.deepcopy(b), cp.deepcopy(c), cp.deepcopy(d)
g[0], f[0], e[0], h[0] = d[0], c[0], b[0], a[0]
FACES[4], FACES[1], FACES[5], FACES[0] = clockwise(e), clockwise(f), antiClockwise(g), clockwise(h)
def _R(FACES):
FACES[3] = antiClockwise(FACES[3])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = antiClockwise(FACES_new[4]), antiClockwise(FACES_new[1]), clockwise(FACES_new[5]), antiClockwise(
FACES_new[0])
e, f, g, h = cp.deepcopy(a), cp.deepcopy(b), cp.deepcopy(c), cp.deepcopy(d)
f[0], g[0], h[0], e[0] = a[0], b[0], c[0], d[0]
FACES[4], FACES[1], FACES[5], FACES[0] = clockwise(e), clockwise(f), antiClockwise(g), clockwise(h)
def R2(FACES):
for i in range(2):
R(FACES)
def F(FACES):
FACES[4] = clockwise(FACES[4])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = clockwise(clockwise(FACES_new[0])), FACES_new[1], antiClockwise(FACES_new[2]), clockwise(FACES_new[3])
e, f, g, h = cp.deepcopy(a), cp.deepcopy(b), cp.deepcopy(c), cp.deepcopy(d)
e[0], g[0], f[0], h[0] = c[0], b[0], d[0], a[0]
FACES[0], FACES[1], FACES[2], FACES[3] = clockwise(clockwise(e)), f, clockwise(g), antiClockwise(h)
def _F(FACES):
FACES[4] = antiClockwise(FACES[4])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = clockwise(clockwise(FACES_new[0])), FACES_new[1], antiClockwise(FACES_new[2]), clockwise(FACES_new[3])
e, f, g, h = cp.deepcopy(a), cp.deepcopy(b), cp.deepcopy(c), cp.deepcopy(d)
g[0], f[0], h[0], e[0] = a[0], c[0], b[0], d[0]
FACES[0], FACES[1], FACES[2], FACES[3] = clockwise(clockwise(e)), f, clockwise(g), antiClockwise(h)
def F2(FACES):
for _ in range(2):
F(FACES)
# 上(0),下(1),左(2),右(3),前(4),后(5)
def B(FACES):
FACES[5] = clockwise(FACES[5])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = FACES_new[0], clockwise(clockwise(FACES_new[1])), clockwise(FACES_new[2]), antiClockwise(FACES_new[3])
e, f, g, h = cp.deepcopy(a), cp.deepcopy(b), cp.deepcopy(c), cp.deepcopy(d)
g[0], f[0], h[0], e[0] = a[0], c[0], b[0], d[0]
FACES[0], FACES[1], FACES[2], FACES[3] = e, clockwise(clockwise(f)), antiClockwise(g), clockwise(h)
def _B(FACES):
FACES[5] = antiClockwise(FACES[5])
FACES_new = cp.deepcopy(FACES)
a, b, c, d = FACES_new[0], clockwise(clockwise(FACES_new[1])), clockwise(FACES_new[2]), antiClockwise(FACES_new[3])
e, f, g, h = cp.deepcopy(a), cp.deepcopy(b), cp.deepcopy(c), cp.deepcopy(d)
e[0], g[0], f[0], h[0] = c[0], b[0], d[0], a[0]
FACES[0], FACES[1], FACES[2], FACES[3] = e, clockwise(clockwise(f)), antiClockwise(g), clockwise(h)
def B2(FACES):
for i in range(2):
B(FACES)
'''
|************|
|*U1**U2**U3*|
|************|
|*U4**U5**U6*|
|************|
|*U7**U8**U9*|
|************|
************|************|************|************|
*L1**L2**L3*|*F1**F2**F3*|*R1**R2**R3*|*B1**B2**B3*|
************|************|************|************|
*L4**L5**L6*|*F4**F5**F6*|*R4**R5**R6*|*B4**B5**B6*|
************|************|************|************|
*L7**L8**L9*|*F7**F8**F9*|*R7**R8**R9*|*B7**B8**B9*|
************|************|************|************|
|************|
|*D1**D2**D3*|
|************|
|*D4**D5**D6*|
|************|
|*D7**D8**D9*|
|************|
'''
def toString(FACES):
print()
for i in range(3):
print(" ", int(FACES[0][i][0]), int(FACES[0][i][1]), int(FACES[0][i][2]))
for i in range(3):
print(int(FACES[2][i][0]), int(FACES[2][i][1]), int(FACES[2][i][2]), end=" ")
print(int(FACES[4][i][0]), int(FACES[4][i][1]), int(FACES[4][i][2]), end=" ")
print(int(FACES[3][i][0]), int(FACES[3][i][1]), int(FACES[3][i][2]), end=" ")
print(int(FACES[5][i][0]), int(FACES[5][i][1]), int(FACES[5][i][2]))
for i in range(3):
print(" ", int(FACES[1][i][0]), int(FACES[1][i][1]), int(FACES[1][i][2]))
print()
def moves(FACES, lst):
for x in lst:
if x == 'U':
U(faces)
elif x == 'u':
_U(faces)
elif x == 'D':
D(faces)
elif x == 'd':
_D(faces)
elif x == 'L':
L(faces)
elif x == 'l':
_L(faces)
elif x == 'R':
R(faces)
elif x == 'r':
_R(faces)
elif x == 'F':
F(faces)
elif x == 'f':
_F(faces)
elif x == 'B':
B(faces)
elif x == 'b':
_B(faces)
lst = input("请输入步骤:")
moves(faces, lst)
print("执行后的魔方为")
toString(faces)
reverse = ''.join(map(chr, map(lambda x: ord(x) ^ 32, lst)))[::-1]
moves(faces, reverse)
print("魔方恢复步骤:", reverse)
toString(faces)
示例
请输入步骤:UBLDFRULFDRULBGBVFDRLLBFLLDSSDBVDJFRUDLRFBDLFBbdj
执行后的魔方为
2 5 3
5 0 2
5 0 5
5 2 3 1 2 1 2 4 0 4 0 0
1 2 3 1 4 5 1 3 1 4 5 2
2 5 2 4 4 3 1 0 5 3 4 4
1 0 4
3 1 3
0 3 0
魔方恢复步骤: JDBbfldbfrldurfjdvbdssdllfbllrdfvbgblurdflurfdlbu
0 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 0
2 2 2 4 4 4 3 3 3 5 5 5
2 2 2 4 4 4 3 3 3 5 5 5
2 2 2 4 4 4 3 3 3 5 5 5
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
Process finished with exit code 0
注:大写为顺时针,小写为逆时针
相关文章
- 163免费邮箱官网直登入口-163免费邮箱海外版快捷登录 12-21
- 夸克网盘如何不限速下载资源-夸克网盘不限速下载资源方法 12-21
- 学信网登录入口-官网安全登录指南(快速便捷的账号登入指引) 12-21
- 漫蛙漫画官方正版入口链接 12-21
- Nano香蕉Pro官网直连入口 Nano香蕉2国内极速直达网址 12-21
- TikTok在线观看视频高清入口-TikTok官网视频流畅播放 12-21