最新下载
热门教程
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
Java并发编程之浅谈ReentrantLock代码示例
时间:2022-06-29 02:25:45 编辑:袖梨 来源:一聚教程网
本篇文章小编给大家分享一下Java并发编程之浅谈ReentrantLock代码示例,文章代码介绍的很详细,小编觉得挺不错的,现在分享给大家供大家参考,有需要的小伙伴们可以来看看。
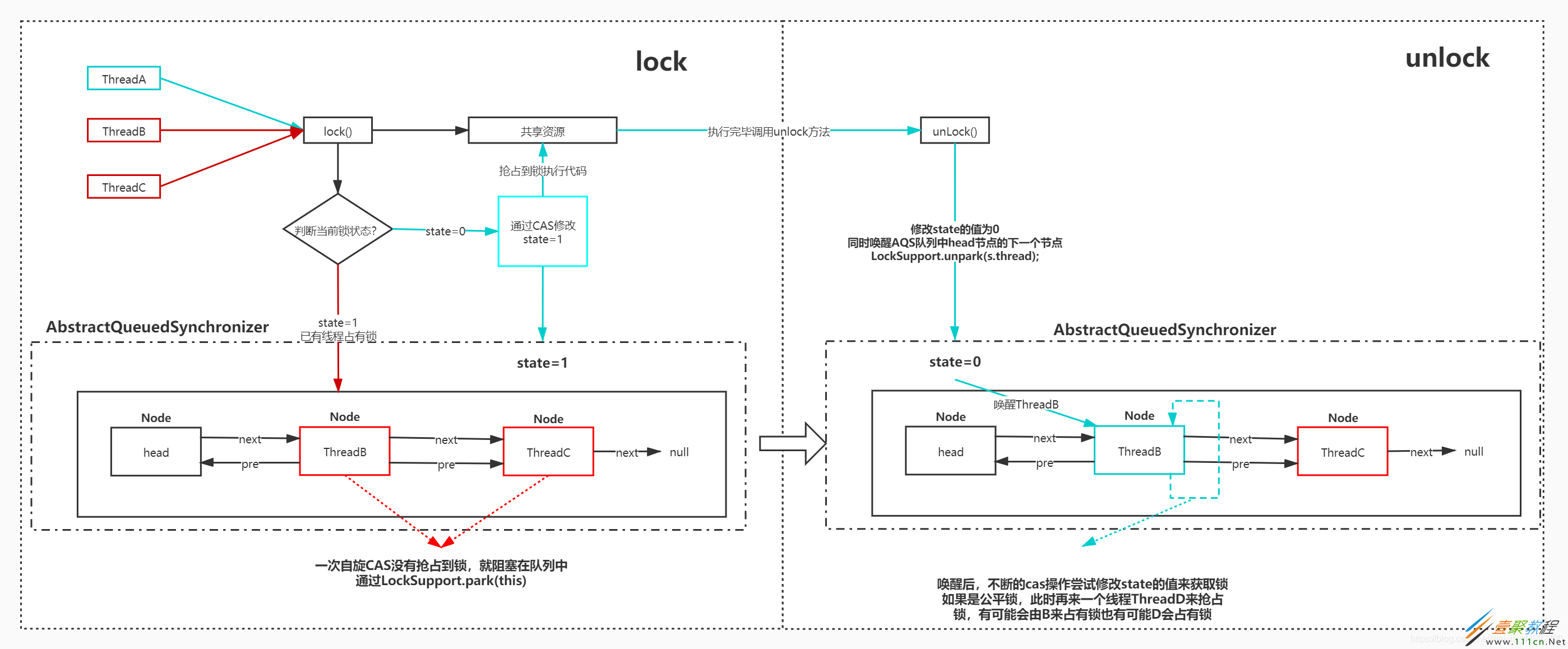
一、首先看图
二、lock()跟踪源码
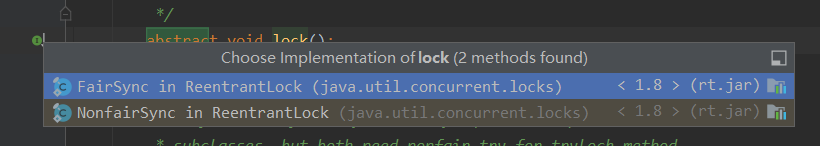
这里对公平锁和非公平锁做了不同实现,由构造方法参数决定是否公平。
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
}
2.1 非公平锁实现
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
代码量很少。首先compareAndSetState(0, 1)通过CAS(期望值0,新值1,内存值stateOffset)
如果修改成功,即抢占到锁,setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());将AQS中的变量exclusiveOwnerThread设置为当前抢占到锁的线程,也就是图中的ThreadA。
若没有抢占成功,证明此时锁被占用,执行方法acquire(1);。
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
这里主要看两个方法tryAcquire(arg)和acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)。当满足if条件后,会给当前线程标记一个interrupt状态。
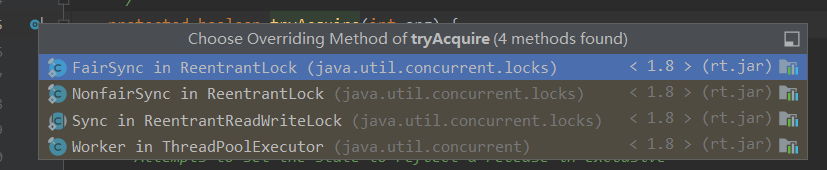
2.1.1 tryAcquire(arg)
这个方法又有多个实现。这里看NonfairSync非公平锁。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
在这个方法中,还不死心,首先会判断下AQS中的state是否为0,为0也就是说距离上次尝试获取锁到现在准备进入队列(双向链表)中这段时间内,锁已经被释放,可以重新CAS尝试获取锁。
如果当前锁还是被持有状态,就是state!=0,就会判断,当前线程是不是当前持有锁的线程exclusiveOwnerThread,如果是,则state+1,从这里可以看出state表示的是重入次数。
全部不满足,返回false。
2.1.2 acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
addWaiter
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
tryAcquire(arg)返回false,证明当前线程还是没有获取到锁。那么就要进入队列等待了,首先addWaiter方法,将当前线程封装成一个Node,如果pred不为空,则将当前节点做链表的尾部插入,同时为了防止在此期间前序节点已经不在队列中了,也会运用CAS操作来执行(期望值pred,新值node,内存值tailOffset)。
如果前序节点为空,或者在CAS时发现前序节点已经不存在了,则重新构建链表,将当前节点封装的Node,加入到链表当中。
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
加入完成后,返回当前node节点,进入acquireQueued方法。
acquireQueued
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
//获取到当前node节点的上一个节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//如果当前的上个节点就是头节点,会再次尝试获取锁
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
//获取成功,将当前节点置空,并成为新的头节点
setHead(node);
//这个p已经没用了,防止内存泄漏,直接指向null,下次GC时回收
p.next = null; // help GC
//不需要取消
failed = false;
//return false,不需要中断当前线程
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
这里是一个自旋操作,首先拿到当前线程封装节点的上一个节点,如果满足第一个if条件if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)),证明上个节点为头节点,则此时当前线程也会再次尝试获取锁,获取锁成功,证明此时没有别的线程在队列中了,则将当前node清空并设置为头节点,返回不需要中断当前线程。
在第二个if条件中if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt())。走到这里证明当前线程不是第一个线程节点,或者没有抢占到锁,shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire这个方法见名知意,在抢占失败后是否需要park阻塞,里面主要是用于清理双向链表中被取消的节点线程和未被阻塞的节点线程。
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;//获取前置节点的等待状态
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
//前置节点的等待状态为-1,表示前置节点在队列中阻塞,那么当前节点也需要被阻塞在队列中
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
//前置节点等待状态大于0,此前置节点已经被取消,循环遍历清除所有已被取消的节点。
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
//前置节点等待状态小于等于0,且不等于-1,也就是没有被阻塞也没有被取消
//则将前置节点设置为阻塞状态。
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
前置节点的等待状态为-1,表示前置节点在队列中阻塞,那么当前节点也需要被阻塞在队列中
前置节点等待状态大于0,此前置节点已经被取消,循环遍历清除所有已被取消的节点。
前置节点等待状态小于等于0,且不等于-1,也就是没有被阻塞也没有被取消。则将前置节点设置为阻塞状态。
到这里,基于非公平锁的实现结束。
2.2 公平锁实现
公平锁和乐观锁的区别就在于,非公平锁acquire(1)前会先尝试获取锁,公平锁直接acquire(1)。
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
}
2.2.1 tryAcquire(arg)
在tryAcquire中也和非公平锁有一定的区别。在当前锁没有被占有时。非公平锁不用考虑目前AQS队列中的排队情况,直接通过CAS尝试获取锁。公平锁会看目前队列的状态,再来决定是尝试占有锁还是在队列中等待。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
相关文章
- 《弓箭传说2》新手玩法介绍 01-16
- 《地下城与勇士:起源》断桥烟雨多买多送活动内容一览 01-16
- 《差不多高手》醉拳龙技能特点分享 01-16
- 《鬼谷八荒》毕方尾羽解除限制道具推荐 01-16
- 《地下城与勇士:起源》阿拉德首次迎新春活动内容一览 01-16
- 《差不多高手》情圣技能特点分享 01-16